

| NEWS | |||||||
| ABOUT | |||||||
| PRODUCTS AND SERVICES | |||||||
|
| |||||||
| PLACE AN ORDER | |||||||
| DOWNLOAD | |||||||
| HELPFUL HINTS | |||||||
| FAQ | |||||||
| LINKS | |||||||
| SEARCH | |||||||
| SITE MAP | |||||||
| CONTACT | |||||||
| русский |
WHAT IS AIR-CONDITIONER
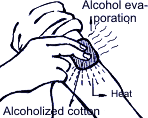
Air-conditioning is control of temperature, humidity, air purification and circulation. Similarly, automobile air-conditioning is not just artificial air cooling but creation of comfortable conditions for a driver and passengers through keeping the micro-climate inside the salon, removal of moisture, dust and dirty air. While skin smearing with alcohol, one can feel coolness; that means that alcohol when evaporating from skin takes away heat. Similarly, coolness appearing after water sprinkling in the yard during the summer-time is explained by evaporation of latent heat taken away from the air above the surface. They say, that in ancient times in India water in the earthenware tub was taken outside for a night. It can be explained by the fact that outside air when adjoining the tub surface takes away latent heat from the water which is gradually evaporated as a result of going through numerous openings of the tub surface and makes the tub water cold. 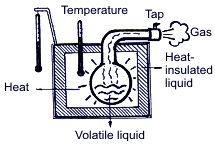
Summing up all the above mentioned, operation of the air-conditioning system is based upon 3 following physical rules: Rule 1. Heat is always transferred from the physical agent with high temperature to the physical temperature with low temperature. Heat is one of energy types, and temperature is one of measuring units of energy value. Rule 2. 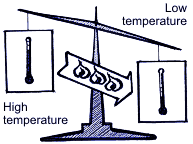 In order to transform liquid into gaseous state, heat is needed. For example, while water evaporating by boiling in a burner, there occurs big heat absorption and the water temperature doesn’t change; on the contrary, when taking away heat from the gaseous matter, it transforms into liquid. The temperature when water is boiling and water vapor results is connected with pressure. Boiling point is increased with pressure increase. 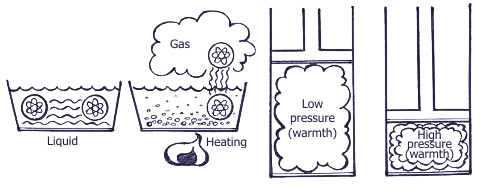 Rule 3. When gas compressing, temperature and gas pressure increase. For example, if in diesel engine the piston is moving upward – downward, the temperature is increasing due to compression. At the same time, if fuel is injected into the cylinder, the blend explosion will occur immediately. If applying the above principles with regard to the basic cooling cycle, then it looks the following way.
High-temperature gas when compressing reaches high temperature, which is much higher than the ambient temperature (rule 3). Ambient air (temperature is lower that temperature of gas in the system) when absorbing heat transforms gas into liquid (rules 1 and 2). Liquid when returning to the initial cycle point is used again.
|
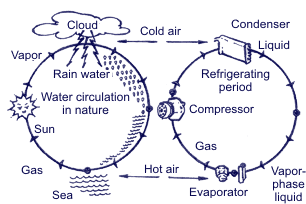 Refrigerant in the liquid state when transforming into the gaseous state absorbs heat from the atmosphere (rules 1 and 2).
Refrigerant in the liquid state when transforming into the gaseous state absorbs heat from the atmosphere (rules 1 and 2).