Components of the air-conditioning system, their organization and check
 Organization and principle of action Organization and principle of action
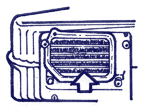
Refrigerant, which has passed through the expansion valve and has become volatile with low pressure, while passing into a misty condition through a branch pipe of the evaporator, under action of the air stream from the fan, after evaporating, turns to gas. Thus, edges of a branch pipe become cold from heat of steam formation, and air inside the automobile becomes cool. Besides the moisture contained in air, from cooling turns to water and together with a dust on the trigger pipeline is thrown out from the automobile.
Since at such heat exchange between the refrigerant and air, the pipeline and edges are used, it is necessary, that water and a dust did not settle on a contact surface with air. Ice and hoarfrost formation on the evaporator occurs as well on parts of edges. At achievement of warm air up to edges, being cooled below temperatures of dew, on edges appear water drops. Thus, in case of cooling of edges up to temperature lower than 0°С, the arisen water drops either freeze, or water air vapors settle as hoarfrost, considerably worsening characteristics of the refrigerating system. Therefore for prevention of freezing of the evaporator, control of a temperature with the regulator or the compressor with a variable pressure is provided.
 Checking Checking
If the surface of the core of the evaporator is creased or it will become covered with layers of dust and external pollution, it will raise resistance of air, in damaged or with cracks the case will damage refrigeration. Besides the hose for release of the condensed water should not be corked, and this is checked in the evaporator: if it is not bent and whether the hose is corked, whether the surface of the pipeline is clean and edges of the evaporator are checked, whether the overpass of the refrigerant was crumpled check, whether edges of the evaporator were crumpled.
|