Components of the air-conditioning system, their organization and check
 Organization and principle of action Organization and principle of action
The condenser is installed before a radiator and carries out function of transformation gaseous high-temperature refrigerant going from the compressor into a liquid condition by allocation of heat in an atmosphere. The amount of heat extracted by the refrigerant in the condenser is defined by the amount of heat absorbed by the evaporator from outside and the work of the compressor necessary for compression of gas. For the condenser the result of heat transfer directly influences the effect of cooling of the refrigerating device, therefore, usually it is installed on the most forward part of the automobile and is deliberately cooled by air of the fan of engine refrigeration system and the air stream arising at movement of the automobile.
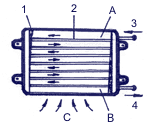 |
1 – refrigeration system fan
2 – pipeline
3 – inlet
4 – outlet
A – gaseous refrigerant
B – liquid refrigerant
C – cooling stream |
|
 Check Check
If the external surface of the condenser will be hammered by a dust and foreign substances, edges will be bent or will break, because of reduction of the amount of proceeding air, pressure inside the condenser may increase up to abnormal value. Therefore the external surface of the condenser should be always pure, and edges should be in the straightened condition.
- Basically, there are two reasons of malfunction of the condenser: outflow and corking. Corking of the condenser is the result of excessive pressure of the compressor. If there are separate sites of corking at passage of these sites from expansion of a coolant sometimes there is an ice or hoarfrost. Let’s say, if air passing through the condenser or a radiator encounters resistance, high head pressure arises.
Attention: at normal work the target pipeline of the condenser is a little bit colder, than the oil pipeline.
|


 Check
Check